Question 24#
A 53-year-old man presents with arthritis, cough, hemoptysis, and bloody nasal discharge. Urinalysis reveals 4+ proteinuria, RBCs, and RBC casts. Chest x-ray shows several bilateral cavitary nodules. CT scan of chest is shown below. ANCA is positive in a cytoplasmic pattern. Antiproteinase 3 (PR3) antibodies are present, but antimyeloperoxidase (MPO) antibodies are absent.
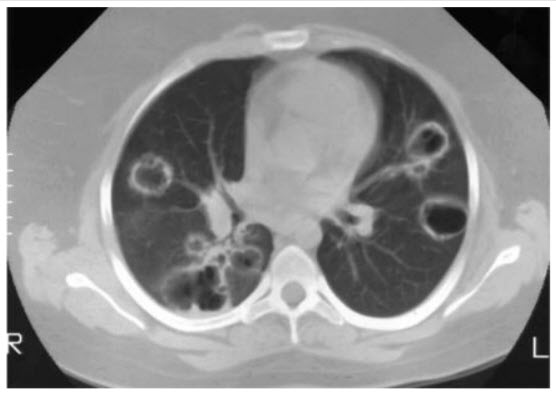
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Behçet syndrome
B. Sarcoidosis
C. Wegener granulomatosis
D. Henoch-Schönlein purpura
E. e. Classic polyarteritis nodosa
Correct Answer is C
Comment:
Wegener granulomatosis (WG) is a granulomatous vasculitis of small- and medium-sized arteries and veins. It affects the lungs, sinuses, nasopharynx, and kidneys, where it causes a focal and segmental glomerulonephritis. Cavitary lung nodules are caused by ischemic necrosis from arterial occlusion. Other organs can also be damaged, including the skin, eyes, and nervous system. Most patients with the disease develop antibodies to certain proteins in the cytoplasm of neutrophils, called antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA). The most common ANCA staining pattern seen in WG is cytoplasmic, C-ANCA. The C-ANCA pattern is usually caused by antibodies to proteinase-3. A perinuclear pattern, P-ANCA, is sometimes seen. P-ANCA is usually caused by antibodies to myeloperoxidase. Behçet syndrome is not associated with ANCA positivity. Henoch-Schönlein purpura and classic polyarteritis do not involve the upper airways and rarely affect the lungs. Sarcoidosis may involve the upper respiratory tract (20%), but it does not cause bloody nasal discharge, cavitary lung disease, or glomerulonephritis.