Question 10#
The ERCP finding that is virtually diagnostic of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) is:
A. A fish-eye lesionB. Calcification
C. Beaded or chain -of-lakes appearance of the duct
D. Cysts that resemble serous cystadenomas
Correct Answer is A
Comment:
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs) usually occur within the head of the pancreas and arise within the pancreatic ducts. The ductal epithelium forms a papillary projection into the duct, and mucin production causes intraluminal cystic dilation of the pancreatic ducts (Fig. below). Imaging studies demonstrate diffuse dilation of the pancreatic duct, and the pancreatic parenchyma is often atrophic due to chronic duct obstruction. However, classic features of chronic pancreatitis, such as calcification and a beaded appearance of the duct, are not present. At ERCP, mucin can be seen extruding from the ampulla of Vater, a so-called fish-eye lesion, that is virtually diagnostic ofiPMN (Fig. below).
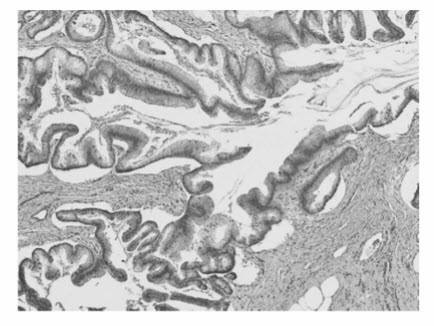
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm histology. Papillary projections of ductal epithelium resemble villous morphology and contain mucin-filled vesicles.
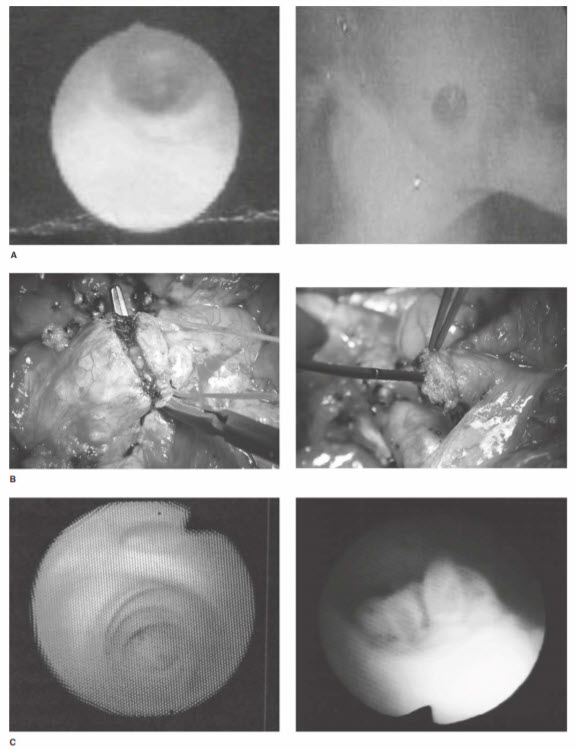
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN). A. Examples of "fish-eye deformity" of IPMN. Mucin is seen extruding from the ampulla. B. Mucin coming from pancreatic duct when neck of pancreas is transected during Whipple procedure (left). Intraoperative pancreatic ductoscopy to assess the pancreatic tail (rig ht). C. Views of pancreatic duct during ductoscopy; normal (left) and IPMN (right).