Question 10#
Which of the following patient groups has a 1000-fold increased risk of developing squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)?
A. Transplant patients on immunosuppressionB. Patients with xeroderma pigmentosa
C. Patients with actinic keratosis
D. Patients exposed to inorganic arsenic
Correct Answer is B
Comment:
SCC is the most common primary malignant tumor of the hand, accounting for 75 to 90% of all malignancies of the hand. Eleven percent of all cutaneous SCC occurs in the hand. It is the most common malignancy of the nail bed. Risk factors include sun exposure, radiation exposure, chronic ulcers, immunosuppression, xeroderma pigmentosa, and actinic keratosis. Marjolin's ulcers represent malignant degeneration of old burn or traumatic wounds into an sec and are a more aggressive type. Transplant patients on immunosuppression have a fourfold increased risk and patients with xeroderma pigmentosa have a 1000-fold increased risk of developing an SCC. They often develop as small, firm nodules or plaques with indistinct margins and surface irregularities ranging from smooth to verruciform or ulcerated (Fig. below). They are locally invasive, with 2 to 5% lymph node involvement. Metastasis rates of up to 20% have been reported in radiation or burn wounds. Standard treatment is excision with 0.5- to 1.0-cm margins. Other treatment options include curettage and electrodessication, cryotherapy, and radiotherapy.
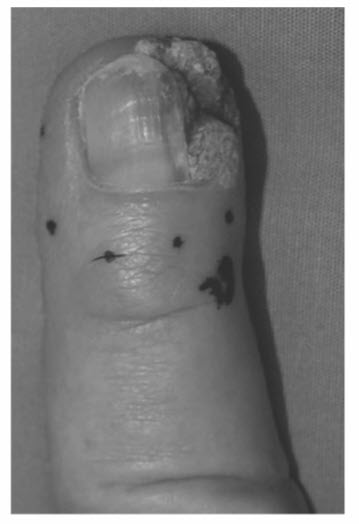
Squamous cell carcinoma involving the nail fold and nail bed. Note the wart-like and ulcerated appearance.