Question 7#
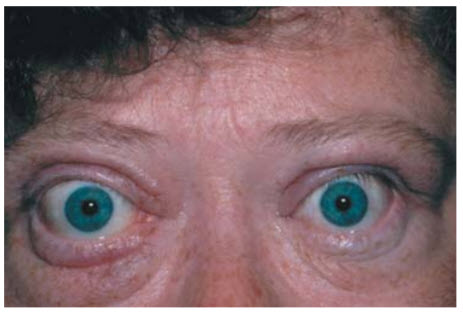
A 32-year-old woman with a history of endometriosis presents with weight loss, diarrhea, and increased appetite for the past 6 weeks. She has a temperature of 37°C, blood pressure of 132/88 mmHg, heart rate of 75 beats per minute, respiratory rate of 18 breaths per minute, and oxygen saturation of 99% on room air. Physical examination reveals a diffusely large, nontender thyroid gland in addition to the findings seen in the photo below (Figure below). Laboratory studies confirm the diagnosis and the patient opts for treatment with methimazole.
Which of the following adverse effects is important to inform the patient of before beginning treatment with this medication?
A. HypocalcemiaB. Acute liver failure
C. Agranulocytosis
D. Vasculitis
Correct Answer is C
Comment:
Agranulocytosis. The patient in this question has been diagnosed with Graves disease and demonstrates exophthalmos and lid retraction. In addition to methimazole, propylthiouracil is another antithyroid drug that can be used in place of radioactive iodine ablation or thyroidectomy. There are several side effects of propylthiouracil and methimazole, several of which are shared by both drugs and some that are unique to each one. Side effects that are shared by both include skin rash, arthralgias, hepatotoxicity, and agranulocytosis. Methimazole can cause jaundice and is teratogenic in the first trimester. (B, D) Propylthiouracil (PTU) can cause vasculitis and is not preferred over methimazole since it carries a risk of acute liver failure. Of note, PTU is preferred during pregnancy. (A) Hypocalcemia is indeed an adverse effect from thyroidectomy, but the patient in this question opted for medical management over surgery.