Question 4#
Which of the following lab results is most consistent with isolated hypoaldosteronism?
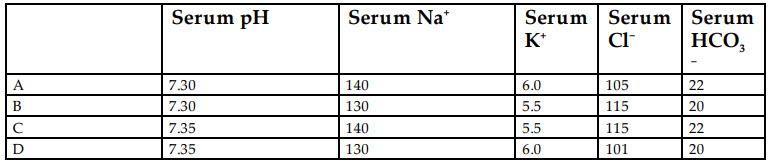
B. B
C. C
D. D
Correct Answer is C
Comment:
Correct Answer: C
Aldosterone is the main mineralcorticoid hormone produced by the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex. It promotes sodium retention and potassium excretion by:
- Upregulating and activating the basolateral Na+ /K+ pump in the distal tubule and collecting ducts.
- Upregulating epithelial sodium channels in the collecting duct and colon.
- Stimulating Na + and water reabsorption from the gut, and salivary and sweat glands in exchange for K+.
- Stimulating secretion of K+ into the tubular lumen.
Hypoaldosteronism presents with hyperkalemia and an associated mild (normal anion gap) metabolic acidosis. Although aldosterone plays a key role in sodium homeostasis, isolated hypoaldosteronism is not typically associated with sodium wasting as the kidney compensates via angiotensin II. Hyponatremia is also uncommon, as ADH is not released in a patient who is otherwise euvolemic. The presence of hyponatremia should warrant workup for primary adrenal insufficiency and other causes. Option C demonstrates eunatremia, mild non-gap metabolic acidosis and hyperkalemia, making it the right answer.
The potassium imbalance in hypoaldosteronism can also impair urinary excretion of ammonium, a condition called type 4 renal tubular acidosis. The most common causes of acquired hypoaldosteronism are hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism, pharmacologic inhibition of angiotensin II or aldosterone, heparin therapy, and critical illness. Hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism is common in patients with mild to moderate renal insufficiency due to diabetic nephropathy or chronic interstitial nephritis but can also occur in acute glomerulonephritis and in patients taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or calcineurin inhibitors. Pharmacologic inhibition of angiotensin II with medications such as ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blocks, and aldosterone receptor blockers are often initiated to improve survival in patients with heart failure and to prevent cardiac remodeling. Heparin has a direct toxic effect on the production of aldosterone in the adrenal cortex. Decreased adrenal production can occur in severely ill patient, whereas stress-induced production of cortisol may divert substrates away from aldosterone production.
Treatment is with replacement therapy with mineralocorticoid effect, such as fludrocortisone.
References:
- DeFronzo RA. Hyperkalemia and hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism. Kidney Int. 1980;17:118.
- Rodríguez Soriano J. Renal tubular acidosis: the clinical entity. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:2160.
- White PC. Disorders of aldosterone biosynthesis and action. N Engl J Med. 1994;331:250.