Question 5#
A 35-year-old asthmatic woman develops an itchy rash over her back, legs, and trunk a few minutes after sitting in a public hot tub. Erythematous, edematous plaques are noted. The wheals vary in size. There are no mucosal lesions and no swelling of the lips.
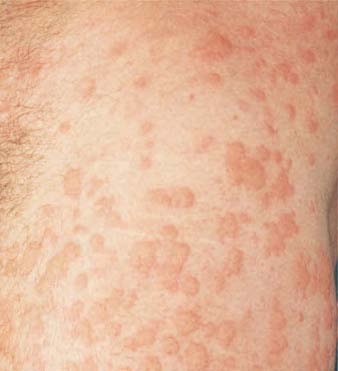
What is the best first step in management of her symptomatic rash?
A. Intravenous glucocorticoidsB. Subcutaneous epinephrine
C. Oral antihistamines (H1 blockers)
D. Aspirin
E. Oral doxycycline
Correct Answer is C
Comment:
Urticaria, or hives, is a common dermatologic problem characterized by pruritic, edematous papules and plaques that vary in size and come and go, often within minutes or hours. In cholinergic urticaria, mast cells may be stimulated by heat, cold, pressure, water, stress, or exercise. Immunologic mechanisms can also cause mast cell degranulation. Patients with atopic conditions, such as asthma or eczema, are more likely to suffer from cholinergic urticaria. Folliculitis caused by P aeruginosa can cause a rash after exposure to hot tubs, but the lesions are not as diffuse, with a line of demarcation depending on the water level, and are usually pustular. This “hot tub” dermatitis begins 8 to 48 hours after exposure to contaminated water (ie, long enough for superficial infection to develop). Systemic antibiotics are seldom necessary, and tetracyclines would be the wrong choice against pseudomonads. Cercarial dermatitis (swimmer’s itch) may occur after swimming or wading in fresh water during spring and summer. Diffuse pruritic papules may appear four to 48 hours after exposure. Treatment is symptomatic. Avoidance of the offending agent, when it is identifiable, is most important in management of urticaria. Oral nonsedating antihistamines provide symptomatic relief and are safely used prophylactically. Glucocorticoids play a minimal role in management of urticaria unless the process is severe and unremitting. Epinephrine plays no role unless there is concomitant anaphylaxis. Agents such as aspirin or alcohol, which aggravate cutaneous vasodilation, are contraindicated.